- Home
- Toxic Chemicals & Health
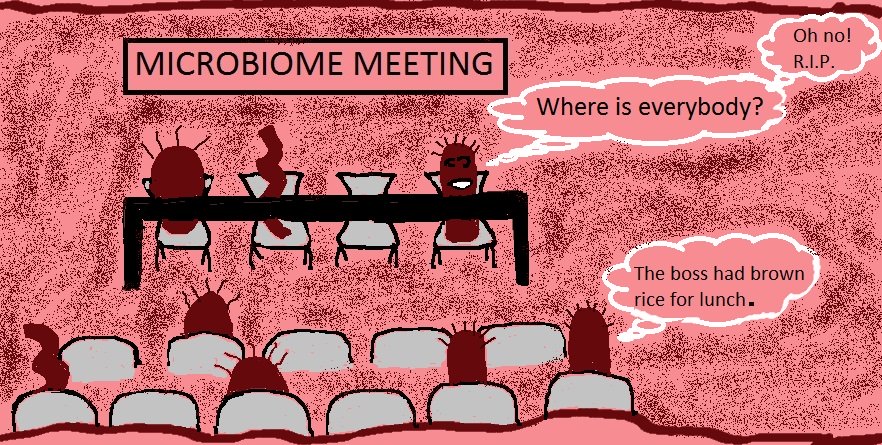
- Chronic Inflammation
Chronic Inflammation - 15 Ways To Quell The Flame
Inflammation is part of your body’s immune response and short-term inflammation (acute) is a good thing. It’s your body’s way to protect itself from foreign invaders like pathogens.
Acute Inflammation involves a group of different responses to a trauma. These responses are triggered in different ways by different things and involve different inflammatory pathways.
But, when your body is constantly bombarded with foreign invaders, including toxic chemicals and pollutants, inflammatory responses can get stuck in overdrive. And that can cause long-term or chronic inflammation. That is the opposite of a good thing.
Why? – Because during the inflammatory process, oxidizing free radicals are formed. (They are also formed during normal cell processes and from exposure to pollutants and toxic chemicals. When your body becomes overwhelmed with free radicals it creates oxidative stress that damages your body.
That’s why there is no doubt in the scientific community that chronic inflammation causes health problems and diseases. These include allergies, asthma, arthritis, cancer, diabetes, Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s, heart disease and obesity.
For Example - The Link Between Inflammation and Cancer
- Inflammation releases free radicals that can damage your cell's DNA.
- Inflammation increases cell division in your body. More cell division increases the risk of mutations.
- Damaged cells are programmed to die. This doesn't happen in inflamed tissue. Instead, cells with precancerous genetic mutations that should have died, live to become cancerous.
There is also no doubt that there are many things that can cause chronic inflammation in your body, some you may not even know about.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
When I started writing this article I checked to see what you wanted to know about inflammation. Besides general information under the search term inflammation, you wanted to know what foods triggered inflammation.
And that’s good that you’re aware of the connection between some foods and body inflammation. There are a lot of foods that trigger inflammation in your body. Things like sugar, foods high in saturated fats like red meat and dairy, trans fats, refined carbohydrates like white flour and foods high in Omega 6 are all sources of body inflammation.
For example, if you eat more sources of Omega 6, (mayo, salad dressings, corn, safflower, soy, peanut and vegetable oils) than Omega 3 (fish, chia seeds), your 6:3 ratio could be high and this creates body inflammation. It’s estimated that the typical American diet creates a ratio of 17:1.
Reducing these items in your diet can help reduce your chronic inflammation. For a great anti inflammatory diet check out the Arthritis Foundation’s The Ultimate Arthritis Diet.
One thing that you were not searching for was the connection between your constant exposure to environmental toxins and the chronic inflammation that this exposure causes. Endocrine disrupting chemicals like BPA and phthalates, pesticides like atrazine and chloropyrifos, POPs (persistent organic pollutants ) like PCBs and PFCs (found in stain and stick resistant products), nanoparticles and toxins in the air have all been linked to body inflammation.
While some toxin exposure is unavoidable, there are ways to reduce your exposure to inflammatory toxins and ways to fight back against chronic inflammation. Read on for 15 ways to reduce your body inflammation.
THE TOXINS YOU’RE EXPOSED TO CAN CREATE CHRONIC INFLAMMATION IN YOUR BODY THAT CAN LEAD TO MANY HEALTH PROBLEMS.
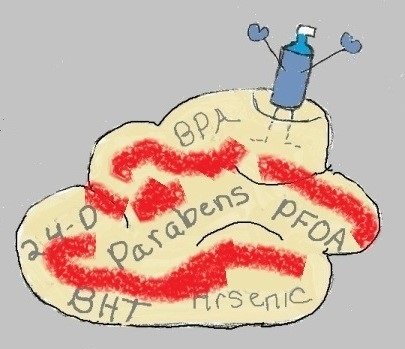
NOTE ABOUT ENDOCRINE DISRUPTING CHEMICALS
Many of the suggestions below will help you reduce your exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals, many of which may cause chronic inflammation. One of the things researchers are discovering is that endocrine disrupting chemicals can affect your immune system, which works closely with the endocrine system, to cause inflammation. And a main source and site of this inflammation is body fat.
Why? Because all the toxins stored in fat make your body fat a target of toxicity. And the main toxic effect triggered by these stored toxins is inflammation. Second, endocrine disrptors also mess with a hormone made in your body fat that protects you from inflammation. This hormone, called adiponectin, reduces tissue inflammation. So any endocrine disrupting chemical that suppresses the release of adiponectin from your fat cells could lead to increased inflammation. BPA, a very common toxin in plastics and the lining of food cans, is an example.
15 Ways To Fight Chronic Inflammation
Clean Up Your Indoor Air
The first 6 ways to reduce chronic inflammation have to do with cleaning up your indoor air. Some toxins that you breathe in create lung inflammation. While outdoor air pollution is definitely a source of lung inflammation, the indoor air in your home and car can be worse.
Any chemicals that are known to cause asthma inflame the lungs. Asthma is an inflammatory disease after all. So air fresheners, cleaning products, plastic chemicals, stain resistant products, candles and pesticides can pollute your indoor air with toxins that cause inflammation.
And scientists are now discovering that there is a connection between chronic lung inflammation and chronic inflammation throughout your body. A good example of this is the link between exposure to high levels of air pollution and heart disease.
To clean up your indoor air:
1. Go Fragrance Free - many of the mystery chemicals that make up fragrance are endocrine disruptors that cause inflammation, including phthalates. Air fresheners, and scented soäps, shampoos, laundry and cleaning products contaminate the air in your home with imflammatory toxins.
Choose fragrance free products whenever possible to clean up your indoor air and reduce your exposure.
2. Adopt Green Cleaning Habits - There are plenty of endocrine disrupting chemicals and chemicals that can inflame your lungs in cleaning products. White vinegar, baking soda, castile soap and a little elbow grease are all you really need to keep your house clean.
3. Use Less Toxic Pesticides - Pesticide exposure creates inflammation in your body. Breathing in the pesticides that you use around your home inflames your lungs. Also, some pesticides are neurotoxins that create inflammation in your brain. This inflammation and the damage it causes can continue for years after exposure.
So give Cedar Oil a try. Diluted in water it will safely control most household and garden pests and eliminate a source of chronic inflammation in your home. For more info on less toxic bug control, check out the pesticide section of Nontoxic For Health.
4. Ditch The Candles - The soot created by burning candles is similar to diesel engine exhaust and second-hand smoke (both are sources of lung inflammation). It contains toxins like toluene, acetone, benzene, styrene, and mercury. Burning a candle also produces nitrogen dioxide, NO2, which causes lung inflammation. Plus, the soot particles are a perfect size to easily infiltrate your lungs.
5. Clean-up Your Laundry Routine - Fabric softeners and laundry detergent contain several types of endocrine disrupting chemicals and chemicals known to cause asthma and allergies. Some of the chemicals in laundry products become airborne and are inhaled when washing and drying and wearing your clothes.
Instead, try less toxic options like GrabGreen 3 in 1 Laundry Detergent Pods, Fragrance Free or least toxic options like homemade laundry detergent. Instead of fabric softener opt for wool dryer balls.
6. Rethink Stain-resistant Carpets, Clothes and Furniture - Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are a class of chemicals that are used to make things stain and stick resistant. Stain-resistant carpeting, furniture and clothing can contaminate your indoor air with PFCs just like cooking with nonstick pans. Studies have found that inhaling the PFCs they emit create body inflammation.
For lots of simple recipes to help you clean up your air, sign up for my free ebook - Homemade Simplified. In the book you'll find 50 recipes that can be made from only 11 cheap and safe ingredients. The simple, practical and economical recipes in this guide will keep your home clean, your home and garden bug-free, and take care of your pups and your skin care needs.
Clean up Your Food (And Your Gut)
7. Eat Organic - Produce that isn't grown organically contains pesticide residues. Sometimes lots of different pesticide residues. Pesticides that you ingest can create inflammation in your gut.
For example, chlorpyrifos, a pesticide used to grow apples, bell peppers, kale, peaches and a lot of other produce, is an endocrine disrupter and a neurotoxin. In mice studies it was found to cause significant gut inflammation, increase intestinal permeability (which means nasty stuff can leak out of your gut and into your blood) and change the types of micro-organisms in your gut.
Chose organic produce whenever possible, especially when it comes to the "dirtiest" fruits and vegetables.
8. Ditch The Can - Canned food is so convenient. BUT, it's also a major source of BPA exposure because it is used to make the epoxy lining in cans. A few companies offer BPA-free cans, but the safety of BPA substitutes is unknown.
In animal studies BPA was found to enter the small intestine immediately after it was ingested, where it causes potent inflammation.
To reduce your BPA exposure, try switching to fresh and frozen products and food packaged in glass and softpaks. This is especial'y important for acidic foods like tomatoes, which cause more BPA to leach from cans.
9. Go Stainless - Toxins emitted from cookware come primarily from non-stick surfaces. Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are a class of chemicals that are used to make things stain and stick resistant. PFCs are released into the air when you use non-sick pots and pans. (Remember all the stories about the dead canaries?)
Stainless steel cookware is a great alternative to non-stick. It browns food better, heats evenly and lasts a lifetime.
10. Ban Plastic - Plastic food containers and water bottles contain many endocrine disruptors like BPA and phthalates. These toxins easily leach into your food and water and then create inflammation as your body deals with them. Plus, some endocrine disrupting chemicals interfere with your body's ability to make the substances that help fight inflammation.
Stainless steel and glass containers and cloth bags are great non toxic food storage options.
11. Heal Your Gut - Trillions of microorganisms live in your gut (a.k.a. your gut microbiome). A healthy gut microbiome improves your health, your immune system and your metabolism. These trillions of little guys also help your body detoxify toxins and maintain the right amount of gut permeability.
Exposure to endocrine disruptors like BPA and pesticides like chlorpyrifos alter your gut microbiome. Help restore it by taking a probiotic like the one I take.
12. Reduce Your Exposure To POPs - Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) stick around for a long time and love to hang out in body fat. When you eat animals (meat and dairy), the POPs in their body fat become your POPs. Because POPs linger for years in your fat, they trigger chronic inflammation in your fat cells.
There are two things you can do to reduce the inflammation caused by POPs - First, reduce the amount of animal fat you eat. Cut down on full fat dairy, red meat and large fatty fish. The second thing you can do is strive for and maintain a lean body mass.
13. Use Clean Sources of Omega 3 - Eating too many sources of Omega 6 and not enough Omega 3 creates an imbalance that causes body inflammation. However, fish, a common source of Omega 3, can also contain high levels of POPs, a source of chronic inflammation.
So don’t rely solely on fish. Opt for less toxic sources of Omega 3, like Chia Seeds, Ground Flaxseed, Hemp Seed and English Walnuts.
14. Clean-up Your Water - What do pesticides, POPs and PFC's have in common? They can all be found in your drinking water, whether it comes from a public water supplier or a private well. So, since you now know that these and other toxins create chronic inflammation, it's a smart move to invest in a water filtering system that will remove as many contaminants as possible.
I keep things simple with a counter top Big Berkey gravity pitcher. This filtering system is stainless steel and each filter is good for 3,000 gallons. So a two-filter system like I have will filter 6,000 gallons. If they get clogged you just scrub them with a brush to unclog
For more information check out - Water Quality And Your Health
15. Add Superfood Benefits To Your Diet - Inflammation creates free radicals. Antioxidant's protect you against free radicals and inflammation. The two sources of antioxidants are the ones your body makes, and the ones in superfoods. So a great way to reduce your chronic inflammation is by adding the antioxidant benefits of superfoods to your diet.
Examples of superfoods include blueberries, beets, ginger, microgreens and sprouts, pomegranate, goji berry, chickpeas, walnuts, almonds, cocoa, broccoli, spinach, Kefir, and bee products like honey, royal jelly, waxes.
The antioxidant benefits of these superfoods come from the small amounts of chemicals called bioactive compounds, found in these foods. These include polyphenols, glucosinolates, carotenoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, saponins, vitamins, and fiber.
Polyphenols are one of the most abundant classes of bioactive compounds found in plant-based foods. Head to the Superfood Benefits Section to learn more.
Acute inflammation protects your body. Chronic inflammation, which can be caused by exposure to many types of toxins, damages your body, and your health. The fifteen steps listed here will help you reduce your exposure to inflammation-causing chemicals.